41 label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf
› pmc › articlesFormation of starch in plant cells - PMC May 11, 2016 · The ae phenotype is characterized by altered amylopectin structure with longer external and internal chains and, in some cases, increased levels of amylose [6, 106, 202, 206–208]. Due to its special swelling and gelatinization properties and reduced digestibility in the digestive tract, ae starch is of special interest both for industry and ... Structure Of A Leaf - Internal & External - The Green Machine Structure Of A Leaf - Internal & External. Margin: This is the outer edging of the leaf. They can be in many different forms, i.e. serrated, parted. Midrib: This is the middle vein of the leaf, it connects with the Petiole. Lateral Veins: These veins are one of the most important parts of the leaf, they transport the food and water the leaf ...
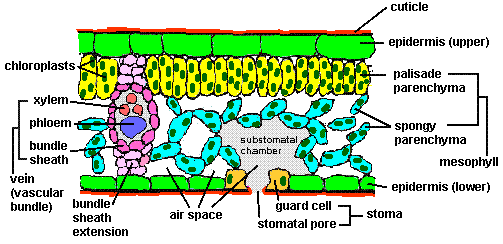
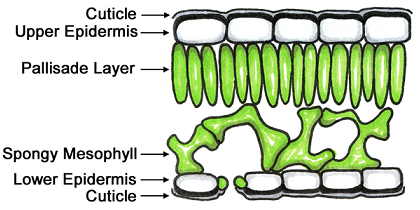
Internal structure of a leaf - SlideShare 1. Internal structure of a leaf • A leaf consists of following layers. • Cuticle • Upper epidermis • Palisade mesophyll • Spongy mesophyll • Lower epidermis • Pores also known as stoma /stomata 2. Cuticle The outer thick waxy covering of the plants and leaves. Cuticle protects plant from drying out by reducing water loss.
Label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf
PDF Label of internal structure of a leaf - wtmongolia.com Cuticle (blue) epidermis (yellow) guard cells (rose) palisade mesophyll (dark green) stranda (purple) xilema (orange) spongy mesophyll (light green) beam sheath (dark blue) at the interior of the leaf, câ € ™ It is a layer of cells called mesophilla. The word Mesophyll is Greek and means  «half» (Meso)  «Leafâ» (Phyllon). chloroplast | Definition, Function, Structure, Location, & Diagram They are enclosed in a chloroplast envelope, which consists of a double membrane with outer and inner layers, between which is a gap called the intermembrane space. A third, internal membrane, extensively folded and characterized by the presence of closed disks (or thylakoids ), is known as the thylakoid membrane. Internal Structure of Leaf (With Diagram) - Biology Discussion The cells occurring beneath the marginal initials, known as submarginal initials, divide in all planes and produce the internal tissues of the leaf. They are often differentiated into three layers—adaxial, abaxial and middle layers. A median procambium develops from the procambial strands of the shoot apex.
Label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf. Chloroplast Stock Photos, Pictures & Royalty-Free Images - iStock Cellular Structure of Leaf Cellular Structure of Leaf. Internal Leaf Structure a leaf is made of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells (called the epidermis) chloroplast stock illustrations ... Biological blue green algae diagram with carboxysome, thylakoid and phycobilisome parts location inside cell ... › previous-year-question-papersLife Processes Class 10 Important Questions and Answers ... Aug 03, 2020 · Draw a neat diagram of internal structure of human heart and label the parts which do the following functions : (a) Chamber where oxygenated blood from lungs in collected, (b) Largest blood vessel in our body, (c) Muscular wall separating right and left chambers. (d) Blood vessel that carries blood from heart to lungs. (CCE 2010, 2012) Answer ... draw and label the parts of a leaf - drmohammadtaha.com Internal structure of a leaf • A leaf consists of following layers. Solution Show Solution. Draw and label the parts of man urinary system? Anatomy of a Leaf, Use These Leaf Parts to Identify a Tree 1. Let us learn about Diversity in the Leaf. !1:))))) - Science - Some Natural Phenomena Label the parts of a leaf - Labelled diagram. Parts of The Internal Structure of A Leaf | PDF save save parts of the internal structure of a leaf for ... stomata phloem xylem cuticle palisade mesophyll spongy mesophyll parts of chloroplast outermembrane inner membrane thylakoid lamella granum stroma food making process photosynthesis light reaction water oxygen nadph atp carbon dioxide calvin cycle sugar label the internal structure of ...
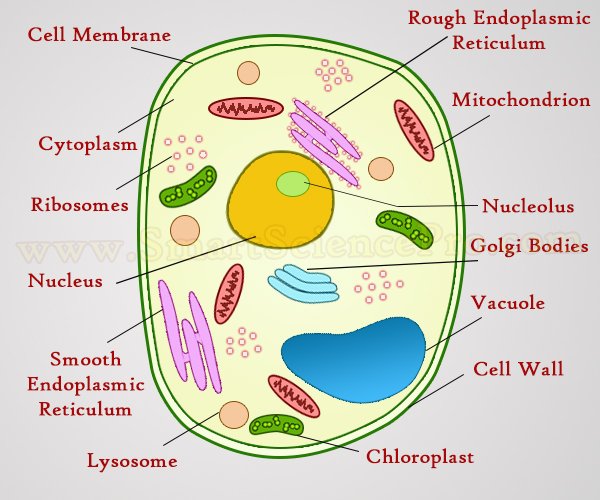
Chloroplast- Diagram, Structure and Function Of Chloroplast The chloroplast structure consists of the following parts: Membrane Envelope It comprises inner and outer lipid bilayer membranes. The inner membrane separates the stroma from the intermembrane space. Intermembrane Space The space between inner and outer membranes. Thylakoid System (Lamellae) The system is suspended in the stroma. LAB-10 Internal Structure of a Leaf and Photosynthesis.docx... Identify the internal structures of a leaf, b. describe the functions of these structures, c. label the parts of the chloroplast ; and d. explain the evidence of photosynthesis Part 1.Internal Leaf Structure: 2. Internal Structure of the Leaf - science.halleyhosting.com Internal Structure of the Leaf of a Typical Dicotyledonous Plant. Internal Leaf Structure a) Cuticle: Waxy layer water proofing upper leaves. b) Upper epidermis: Upper layer of cells.No chloroplasts. Protection. c) Palisade Mesophyll: Tightly packed upper layer of chloroplast containing cells. d) Spongy Mesophyll: Lower layer of chloroplast containing cells. › 1814485 › Taiz_and_Zeiger_Plant(PDF) Taiz & Zeiger- Plant Physiology | Munish K Bansal ... Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
Leaf Structure and Function - Advanced ( Read ) | Biology | CK-12 ... A cross section of a leaf shows that it is a complex organ built of several different kinds of specialized tissues. The tissues, in turn, are built of specialized cells, and the cells, of organelles. Epidermis covers the upper and lower surfaces of the leaf. Usually a single layer of tightly-packed cells, the epidermis mediates exchanges ... Chloroplast: Structure and Function - Biology Wise Chloroplasts are plastids that contain a network of membranes embedded into a liquid matrix, and harbor the photosynthetic pigment called chlorophyll. It is this pigment that imparts a green color to plant parts, and serves to capture light energy. A detailed account of the structure and functions of chloroplasts has been provided below. Functions of the internal parts of a leaf? - Answers Leaf Parts & Function. Lower epidermis - outmost tissue on the lower side of the leaf; protects the leaf. Upper epidermis - outmost tissue on the upper side of the leaf; protects the leaf ... Leaf structure - Plants - GCSE Biology (Single Science) Revision - BBC ... They also open or close to control the loss of water from leaf by the process of transpiration. Absorbing light energy Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll tissue of the leaf....
photosynthesislessonplans.weebly.com › lesson-1Lesson 1: Introduction to Plants - LESSON PLANS FOR GRADE 10 ... It has the function of attaching the leaf to the stem. The petiole has the same internal structure as the stem. It is sometimes called mini-stem. Stem: Located above the soil surface, a stem is one of two main structural axes of a plant. The stem is divided into two parts: nodes and internodes.
Leaf anatomy | Both Internal and External with Labelled Diagram Anatomy of the leaf is the detailed study of the internal structure of a leaf, usually revealed by its dissection. Leaves are responsible for converting sunlight and carbon dioxide into glucose, which is used to provide energy to the plant. Leaves are classified into mainly two types based on their structure, dorsiventral and isobilateral.
Label the parts of chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf Following are the parts of chloroplast: 1) Envelope or outer membrane- semi-porous in nature and permeable to small molecules and ions but it is not permeable to larger proteins. 2) Intermembrane space- it is a thin space of 10-20 nanometers which is present between the outer and inner membrane of chloroplast.
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Cell_(biology)Cell (biology) - Wikipedia Cell Movements and the Shaping of the Vertebrate Body Archived 2020-01-22 at the Wayback Machine in Chapter 21 of Molecular Biology of the Cell Archived 2017-09-27 at the Wayback Machine fourth edition, edited by Bruce Alberts (2002) published by Garland Science. The Alberts text discusses how the "cellular building blocks" move to shape developing embryos. It is also common to describe small ...
Label the part of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf Label the part of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf - 6862374 balasetrisha ... Junior High School answered Label the part of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf 1 See answer Advertisement Advertisement nmariel915 nmariel915 yannnnnnnnnn sana po makatulong hihi. kulang ka sa chloroplast dba 5 un. no4. stroma at ...
Label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf Chloroplasts are very important parts of the cell, they are often called the food producers and they keep cell alive. There are several layers or parts of a chloroplasts and these are inner membrane, outer membrane, stromal lamellae, thylakoid, stroma and starch or sugar. Chloroplasts converts the suns energy into sugar for surviving purposes.
Leaf structure - Structure of plants - WJEC - GCSE Biology ... - BBC the ability to absorb light energy efficiently Absorbing light energy Light absorption happens in the palisade mesophyll tissue of the leaf. Palisade cells are column-shaped and packed with many...
Internal Structure of Leaf: Parts, Function, Diagram - Embibe The anatomy or internal structure of dicot leaves can be understood on the basis of the following structures: 1. Upper Epidermis 2. Mesophyll a. Palisade Tissue b. Spongy Tissue 3. Vascular Tissue 4. Midrib 5. Lower Epidermis Upper Epidermis 1. The upper epidermis is made up of a single layer of parenchymatous cells. 2.



Post a Comment for "41 label the parts of a chloroplast and the internal structure of a leaf"